
Shifting Demographics in Shandong Province: Trends, Challenges, and Future Prospects


 Official data on GDP, disposable income, and population in Hunan Province for 2024
Official data on GDP, disposable income, and population in Hunan Province for 2024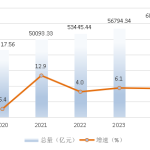 Hubei Province 2024 National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin
Hubei Province 2024 National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin